
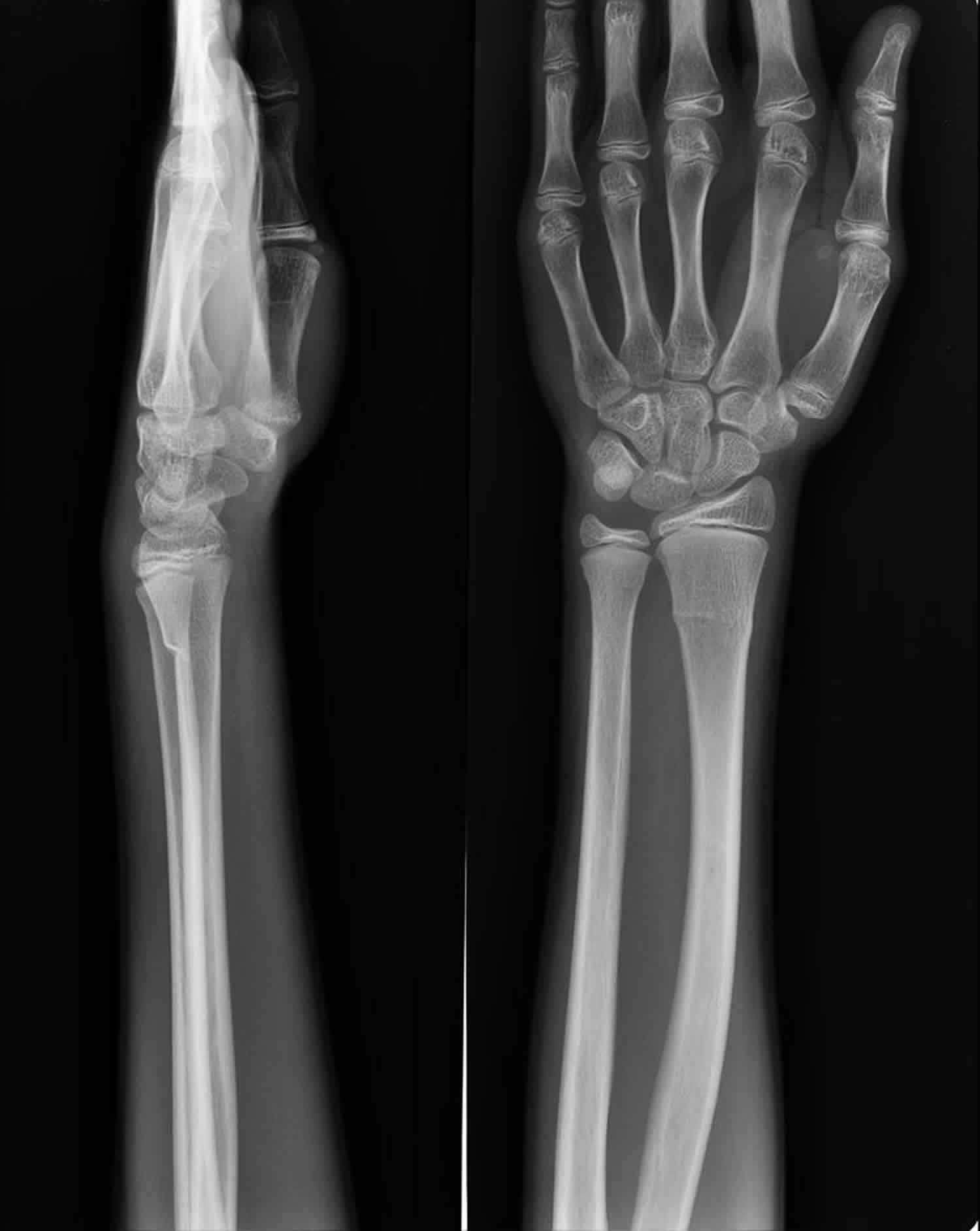
The possibility of non-accidental injury should be considered.ĭocumentation of neurovascular status is essential before and after any intervention, including cast or splint application. Past history may provide insight into pathological fractures. 3 Additional injuries should be sought, such as a distal humerus fracture in association with a fracture at the wrist. It is important to remember that wrist sprains are uncommon in children. The mechanism of injury may suggest the likelihood of fracture as well as type of fracture sustained. The aim of this article is to provide an overview of management concepts and support general practitioners to confidently manage these fractures and refer to orthopaedic services when required. 2įracture management is guided by the fracture pattern and remodelling potential. For children over the age of eight years, the distal radius is the site of 25% of all fractures. 1,2 Forearm fractures occur at a rate of 1.5 per child, with the ratio of affected boys to girls increasing to 5.5:1 at adolescence. The radius and ulna are the long bones fractured most commonly in school-aged children, accounting for 40% of fractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
